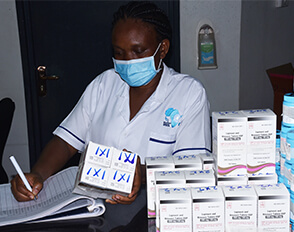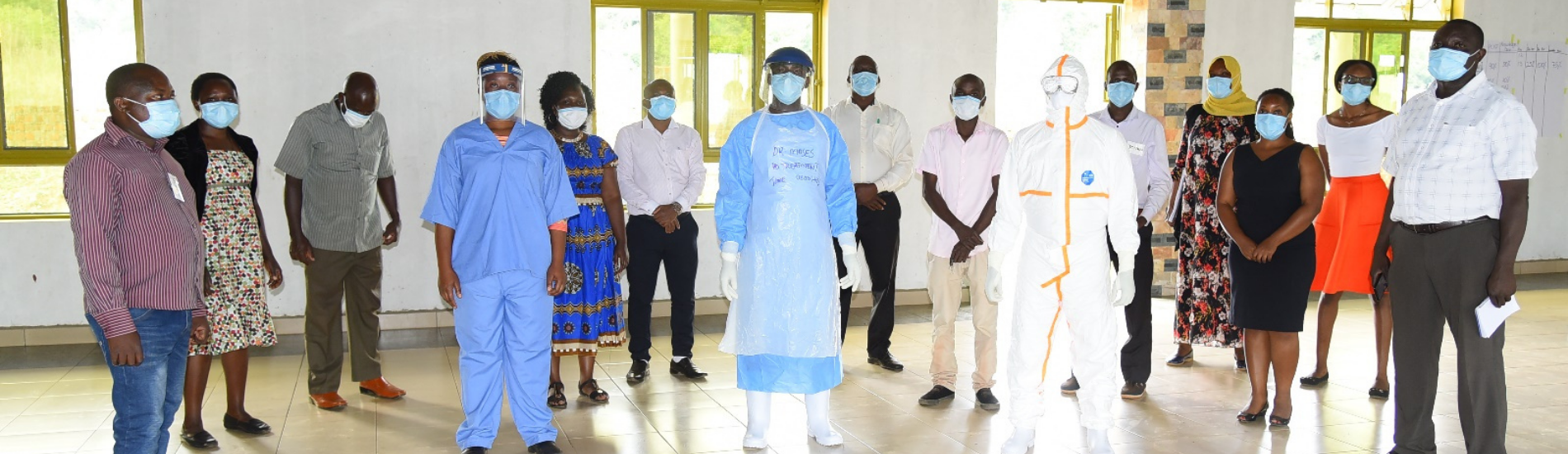
IDI Supports Infection Prevention and Control Training of Mentors in Buvuma District
On the 20th of March 2020, Uganda registered her first COVID-19 case and by 31st of August 2020, the cases had increased to over 3000. This increase and the high rate of community spread has necessitated the demand for better healthcare services across the country.
In an effort to build the capacity of healthcare workers, the Ministry of Health in collaboration with implementing partners developed a National Action Plan for Infection Prevention and Control (IPC) for COVID-19. This plan prescribes entry into all regions through the regional referral hospitals where team trainers are oriented to support trainings at the district level. District team capacity is then built to cascade skills and knowledge to health workers in the health facilities within the districts. IPC is a major aspect in the reduction of the spread of COVID19 with three major goals: Protecting health workers, the community and patients
With funding from Resolve to Save Lives, the IDI Global Health Security program in collaboration with the World Health Organization and Makerere University Water Reed Project (MUWRP) supported the training of mentors in Buvuma District. The district is made up of 52 islands and 9 of these host health facilities, with the first COVID-19 case registered in May and 14 currently confirmed cases.
The mentorship training took place from 1st to 4th September 2020 at Palm Resort near the district headquarters. The district health officer, Dr Ahmed Kanyike selected 13 participants composed of the district health team as well as representatives from different health facilities.
“Representation from health facilities was triangulated according to the sub-counties in the district. Such an arrangement is not only cost-saving but also saves mentors long-distance journeys to an allocated facility“. Maureen Kesande, one of the trainers.
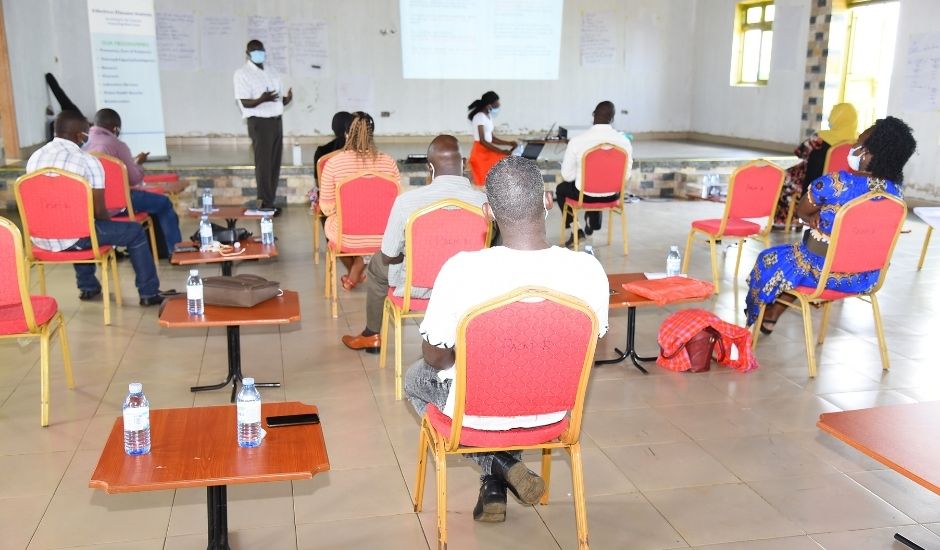

Participants attending one of the theory sessions
The training was comprised of both theory and practical sessions. Some of the topics covered include an overview of COVID-19, IPC, screening, isolation, notification. Standard precautions, the role of an IPC program in the prevention of healthcare-associated infections in quarantine facilities and Points of Entry among others were also covered. The impact of this intervention in health facilities is measured by use of a MOH assessment tool Open Data Kit (ODK) which was installed on mentors’ mobile phones. Baseline results are compared with subsequent results to demonstrate IPC structural gains.
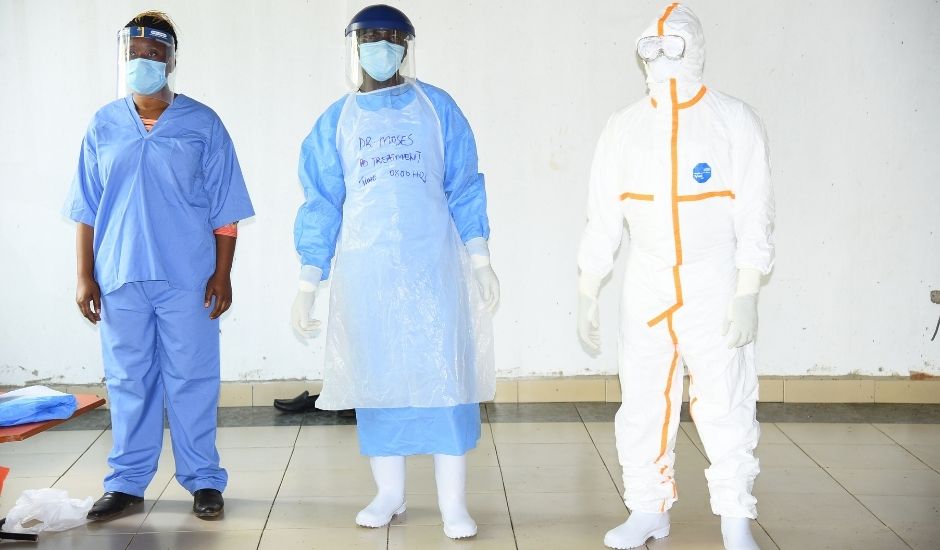
A practical session on Donning and Doffing of Personal Protective Equipment (PPE)
With proper practice of IPC in health facilities as well as in the community, the rate of spread of infection can be greatly reduced. The Ministry of Health has been able to reach over 86 districts through these trainings.
The IDI Global Health Security program continues to support the Ministry of Health mandate to mitigate the impact of infectious disease outbreaks such as the COVID-19 global pandemic through capacity building in the laboratory, surveillance and one health platforms among others. This is done through frontline response, capacity development and many more activities with support from implementing partners to facilitate operation in different health systems.
By Rebecca Nakitandwe
Photography by Abubaker Kazibwe